Prepare Linux Instances for Provider Installation
This guide will walk you through setting up and deploying a provider using Ansible. The steps cover installation on a local system, configuring a remote server, and managing deployments. This document provides best practices and recommendations for doing so.
Pre Requisites
- A Linux server with Ubuntu 22.04.
- Ansible installed on your local machine.
- Basic knowledge of server administration, Ansible, and Kubernetes.
- A public IP is required for the provider to work.
- A domain is required for the provider to work.
- Minimum of 32 CPU, 128 GB RAM and 750 GB+ boot disk is required for the provider to work.
To install Ansible on a Mac, you can use various methods such as Homebrew, pip, or by installing it from source. Here are the steps for each method:
Note: The first 1, 2, & 4 sections need to be done outside the server and it can be your personal laptop / desktop but shouldn’t be inside the server, and then SSH to a remote server to set up everything for the provider.
Note: We have observed that the installation is only compatible with Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy. Please ensure you are using this specific version and not any other.
1. Setup Ansible Using Homebrew
Install Homebrew
If you haven’t installed Homebrew yet, open Terminal and run:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"Install Ansible
Once Homebrew is installed, run:
brew install ansibleAlternatively, if you have Python installed, you can use:
pip install ansibleFor other distributions, refer to the Ansible Community Documentation for specific installation instructions.
Verify the Installation
Check the version of Ansible to confirm it’s installed:
ansible --version2. Setup Domain for the Provider
Note: Before attaching a domain for the provider setup, we recommend avoiding domains with the TLD .dev or .app. These domains are always redirected to HTTPS due to a Google initiative, and since SSL is not yet supported by Spheron Providers, deployments using these TLDs will not work for users.
Create the following name entries on your domain provider.
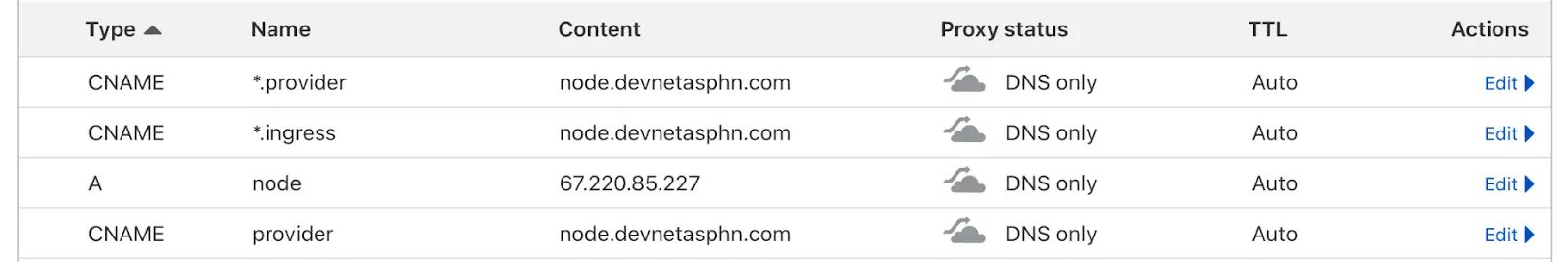
This is the records you need to put for your domain - yourdomain.com
| Type | Name | Content |
|---|---|---|
| CNAME | *.provider | node.yourdomain.com |
| CNAME | *.ingress | node.yourdomain.com |
| A | node | <Your Public IP> |
| CNAME | provider | node.yourdomain.com |
3. Firewall & Port Policy for Master node
To ensure the master node on your provider functions correctly, you must expose specific TCP ports on your server. The required configuration includes:
- TCP Ports Range: Open all TCP ports from 1000 to 65535. This wide range ensures that all necessary communications and services can operate without restriction.
- Standard Web Ports:
- Port 80: This port is typically used for HTTP traffic, allowing web services to be accessible over the internet.
- Port 443: This port is used for HTTPS traffic, ensuring secure, encrypted communications for web services.
By exposing these ports to the internet, you enable the master node to interact with various components and services, ensuring seamless operation and connectivity.
Steps to Expose Ports
- Firewall Configuration: Adjust your firewall settings to allow inbound and outbound traffic on the specified ports.
- Network Settings: Ensure that your network configuration (e.g., router, security groups) permits traffic on these ports.
- Server Security: Regularly monitor and secure these ports to protect against unauthorized access and potential vulnerabilities.
Following these steps will help maintain the proper functionality and security of your master node on the provider.
4. Prepare Linux Instance for Installation Using Ansible
Step 1: Clone the Repository
Clone this repo onto your local system: GitHub - spheron-core/provider-installation
git clone https://github.com/spheron-core/provider-installationRepo has the following file structure:
- README.md
- Readme.md
- inventory.ini
- playbook.yml
- add-agent.sh
- k3s-bootstrap.sh
- only-provider.sh
- start-spheron.sh
Step 2: Edit Inventory File
Now, edit the playbook/inventory.ini file with your server details, Example:
[testnet]
server-name ansible_host=23.158.40.38 ansible_user=root ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.ssh/id_rsaProperly set up server IP, user_name, and the SSH key. Make sure the SSH key has access to the server you just filled.
Step 3: Edit Playbook
Now edit the hostname in playbook/playbook.yaml
hostname: provider.example.com ## this can be your registered domain name that will be used for the providerStep 4: Execute the Playbook
Now execute the playbook
cd playbook
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbook.ymlAfter the whole execution, the server will restart.